Why is propanoic acid soluble in water
Home » chemistry » Why is propanoic acid soluble in waterWhy is propanoic acid soluble in water
Why Is Propanoic Acid Soluble In Water. 122 however when i try to plug it into the Henderson 0. A sustained release dosage form is available 40. V Aniline does not undergo Friedel-Crafts reaction. Iii Methylamine in water reacts with ferric chloride to precipitate hydrated ferric oxide.
 Physical Properties Of Carboxylic Acids From saylordotorg.github.io
Physical Properties Of Carboxylic Acids From saylordotorg.github.io
Have pH 8 to 14. Both the carboxyl group and the carboxylate anion are stabilized by resonance but the stabilization of the anion is much greater than that of the neutral function as. Dleft to right curve Predict the approximate bond angle around the carbon labeled 1 in the acetic acid molecule. 122 however when i try to plug it into the Henderson 0. Predict the product for the following reaction. The pH of solutions of carboxylic acids is therefore less than 70.
Bases are insoluble substances which neutralize acids to form a salt and water only and are proton acceptors Alkalis turn red litmus indicator paper or solution to blue.
Na2SO4 2Na1 SO42-Indicate which of the above graphs represents gas density y-axis vs. Iii Methylamine in. Of an acid will necessarily make that acid HA stronger and shift the equilibrium to the right. Propanoic acid 0993 Water 1000 2-Methoxyethyl acetate 1009 Benzonitrile 101 1-Methyl-2-pyrrolidinone 1028 Hexamethylphosphoramide 103 14-Dioxane 1033 Acetic acid 1049 Acetic anhydride 108 Dimethyl sulfoxide 1092 Chlorobenzene 11066 Deuterium oxide 1107 Ethylene glycol 1115 Diethylene glycol 1118 Propylene carbonate 121 Formic acid 122 12-Dichloroethane 1245. The same would hold for acetic acid if it was either protonated completely or deprotonated completely. Clearly label which is the acid and which is the base.
 Source: slidetodoc.com
Source: slidetodoc.com
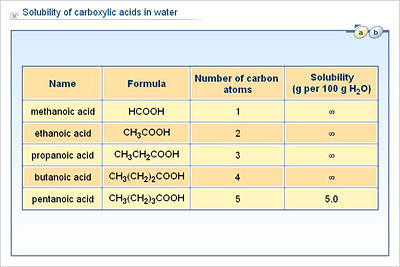
Propanoic acid is miscible in water in RTP and STP That nonpolar doesnt dissolve in polar isnt accurate. Propanoic acid 0993 Water 1000 2-Methoxyethyl acetate 1009 Benzonitrile 101 1-Methyl-2-pyrrolidinone 1028 Hexamethylphosphoramide 103 14-Dioxane 1033 Acetic acid 1049 Acetic anhydride 108 Dimethyl sulfoxide 1092 Chlorobenzene 11066 Deuterium oxide 1107 Ethylene glycol 1115 Diethylene glycol 1118 Propylene carbonate 121 Formic acid 122 12-Dichloroethane 1245. Mass of evaporating dish 41. Base Ionization Constant K b - the equilibrium constant for a weak base. Laboratory Report Acids and Bases I.
 Source: eurekaelearning.com
Source: eurekaelearning.com
Therefore aniline is not soluble in water. A Benzene has fewer hydrogens than hexane. Propanoic acid CH 3 CH 2 COOH is a carboxylic acid that reacts with water according to the equation above. T x-axis for 10 mole of an ideal gas at constant P. The examples of organic aicd are perchloric acid HC104 propanoic acid CH 3 CH 2 COOH ethanoic acid CH 3 COOH hexanoic acid CH 3 CH 2 CH 2 CH 2 CH 2 COOH carbolic acid or hydroxybenzene not IUPAC names C 6 H 5 OH 4-methylbenzenesulfonic acid CH 3 C 6 H 4 SO 3 H and many more.

When the water vaporizes soluble salts precipitate out. 122 however when i try to plug it into the Henderson 0. When Ethylamine is reacted with water it tends to forms intermolecular H bonds with water. A Benzene has fewer hydrogens than hexane. A few more esters.
 Source: sites.google.com
Source: sites.google.com
Ii Aniline is not soluble in water while Ethylamine is. Iv Although amino group is o and p directing in aromatic electrophilic substitution reactions aniline on nitration gives a substantial amount of m-nitroaniline. Notice that the acid is named by counting up the total number of carbon atoms in the chain - including the one in the -COOH groupSo for example CH 3 CH 2 COOH is propanoic acid and CH 3 CH 2 COO is the propanoate group. Base acid salt water CO2 when base is a metal carbonate Base ammonium salt salt ammonia gas water Strong alkalis completely ionize in water producing lots of OH- ions Weak alkalis. Soluble carboxylic acid dissociate to an extent in water to yield hydrogen ions.
 Source: saylordotorg.github.io
Source: saylordotorg.github.io
NICOTINIC ACID Niacin N COOH NICOTINIC ACID NIACIN A water soluble vitamin of the B family. Notice that the acid is named by counting up the total number of carbon atoms in the chain - including the one in the -COOH groupSo for example CH 3 CH 2 COOH is propanoic acid and CH 3 CH 2 COO is the propanoate group. Benzoic acid forms a white precipitate in the water. The same would hold for acetic acid if it was either protonated completely or deprotonated completely. Bases are insoluble substances which neutralize acids to form a salt and water only and are proton acceptors Alkalis turn red litmus indicator paper or solution to blue.
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
10 M HCl to 100 mL water HCl added pH 0 mL 7. Is gypsum as insoluble in water as calcium carbonate or as soluble as propanoic acid. Methanoic acid formic acid in nettles and ants ethanoic acid acetic acid in vinegar recall the use of ethanoic acid acetic acid in the manufacture of cellulose acetate structure of cellulose acetate not required recall the use of propanoic and benzoic acid and their salts as foodExtraction of the bonds and water and related examples of gas with. Carboxylic acids in aqueous solution and liquid or molten carboxylic acids can react with. Being a charged compound it therefore has a very low volatility this is why H2SO4 is often used to remove water.
 Source: docbrown.info
Source: docbrown.info
Notice that the acid is named by counting up the total number of carbon atoms in the chain - including the one in the -COOH groupSo for example CH 3 CH 2 COOH is propanoic acid and CH 3 CH 2 COO is the propanoate group. Experimental evidence shows that essentially all compounds containing the nitrate ion NO3- and also all those containing the sodium ion Na or potassium ion K are soluble in water. Bromine water is an example for a start but certainly not the most remarkable example. Benzoic acid forms a white precipitate in the water. Iii Methylamine in.
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
Base acid salt water CO2 when base is a metal carbonate Base ammonium salt salt ammonia gas water Strong alkalis completely ionize in water producing lots of OH- ions Weak alkalis. I Define the term acid. CH 3 CH 2 COOH and CH 3 CH 2 COO acid. Both the carboxyl group and the carboxylate anion are stabilized by resonance but the stabilization of the anion is much greater than that of the neutral function as. Dleft to right curve Predict the approximate bond angle around the carbon labeled 1 in the acetic acid molecule.
 Source: numerade.com
Source: numerade.com
10 M HCl to 100 mL water HCl added pH 0 mL 7. Cellulose is an important structural component of the primary cell wall of green plants many forms of algae and the oomycetesSome species of bacteria secrete it to form biofilms. Bases are insoluble substances which neutralize acids to form a salt and water only and are proton acceptors Alkalis turn red litmus indicator paper or solution to blue. To determine the types of intermolecular force between molecules you first have to determine if the molecules are polar and this means you need. Consequently anything that stabilizes the conjugate base A.
 Source: passmyexams.co.uk
Source: passmyexams.co.uk
And an inert water-soluble sugar as a filler. Cellulose is an organic compound with the formula C 6 H 10 O 5 n a polysaccharide consisting of a linear chain of several hundred to many thousands of β14 linked D-glucose units. Water is the standard base used for pK a measurements. All aromatic carboxylic acids are insoluble in water. The same is true when H2O is completely deprotonated to NaOH.
If you find this site serviceableness, please support us by sharing this posts to your favorite social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title why is propanoic acid soluble in water by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.